-
Technical Notes

-
Field applicability evaluation of surface treatment construction method to prevent anti-ice on road surfaces in winter
겨울철 도로 노면의 살얼음방지를 위한 표면처리 시공방법에 대한 현장 적용성 평가
-
Kyong Il Ko, In Woo Shin, Dong Min Cho, Hyun kuk Shin
고경일, 신인우, 조동민, 신현국
- The anti-icing surface treatment method is a method developed to prevent slippery traffic accidents caused by ice-forming and black ice on road …
- The anti-icing surface treatment method is a method developed to prevent slippery traffic accidents caused by ice-forming and black ice on road surfaces in winter. In this study, an anti-icing surface treatment material mixed with Grikol, an anti-icing agent, and MMA resin was used for on-site construction. In order to evaluate the performance of the anti-icing surface treatment method, a freezing bond strength test and a skid resistance test were conducted to analyze the on-site applicability. As a result, the freezing bond strength satisfied the standard of 0.1 MPa up to -6°C. In the case of the skid resistance test, it was confirmed that all the standards satisfied the general section SN ≥ 35 standard. Based on the on-site tracking investigation, it was confirmed that the anti-icing surface treatment method exhibited anti-icing performance even at temperatures up to -6°C. - COLLAPSE
-
Field applicability evaluation of surface treatment construction method to prevent anti-ice on road surfaces in winter
-
Technical Notes
-
3D X-ray CT-based deterioration performance evaluation method of asphalt
3D X-ray CT기반 아스팔트의 열화 성능 평가방법
-
Yeon Jong Jung
정연종
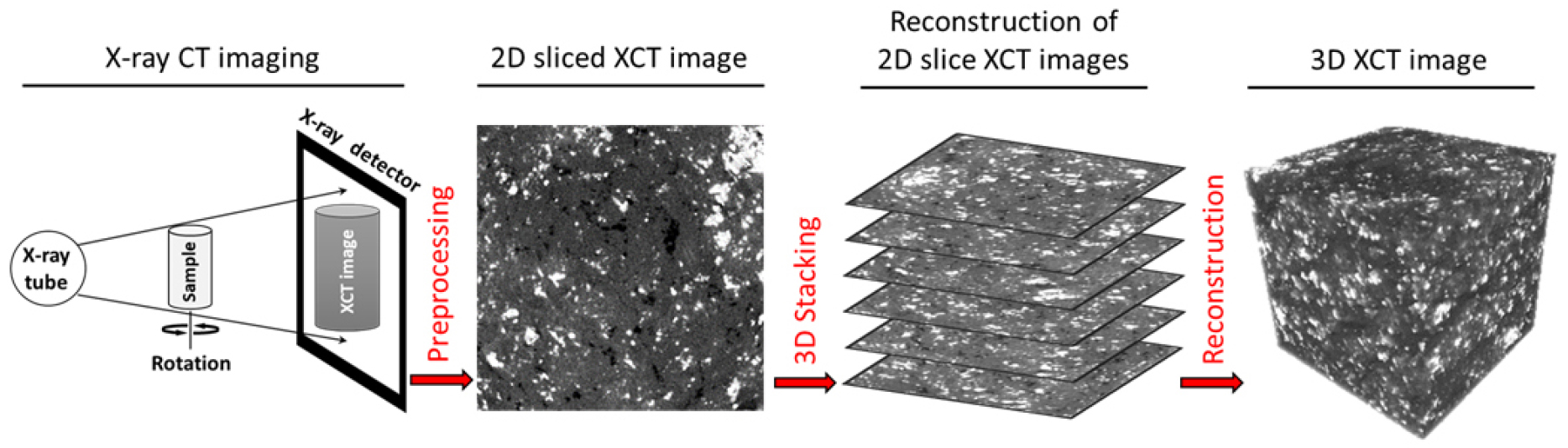
- This paper presents a methodology for evaluating the degradation performance of asphalt using 3D X-ray Computed Tomography (XCT). Inspired by previous studies …
- This paper presents a methodology for evaluating the degradation performance of asphalt using 3D X-ray Computed Tomography (XCT). Inspired by previous studies on cement reaction rates, this research aims to quantify and model the degradation of asphalt. Asphalt samples are exposed to various environmental stress conditions, and high-resolution 3D images are captured at each degradation stage. These images visualize the internal structural changes of the asphalt and allow for a quantitative analysis of the degradation mechanisms. The study systematically explains the procedures for sample preparation, curing conditions, environmental stress factors, 3D XCT imaging, image analysis, and data interpretation. Samples are exposed to stress factors such as freeze-thaw cycles, moisture saturation, and chemical exposure, and 3D images are obtained at each time stage to measure changes in density, porosity, and crack propagation. The data obtained is used to understand the degradation mechanisms and develop models to predict the long-term performance of asphalt. This methodology combines high-resolution imaging and quantitative analysis to provide more accurate and reliable results in evaluating asphalt durability. This can contribute to the development of more robust and durable road pavement materials. - COLLAPSE
-
3D X-ray CT-based deterioration performance evaluation method of asphalt
-
Scientific Paper

-
Effect of stage mixing on rejuvenation level of binder in warm-mix recycled asphalt mixture
단계적 혼합이 중온순환아스팔트혼합물의 바인더 회생에 미치는 영향
-
Wonbae Kim, Woohyun Kim, Kwang W. Kim
김원배, 김우현, 김광우
- In this study, a RAP was used for preparing a warm-mix recycled mix with a bio-warm-mix asphalt rejuvenator (BWR) using the stage …
- In this study, a RAP was used for preparing a warm-mix recycled mix with a bio-warm-mix asphalt rejuvenator (BWR) using the stage mixing (STM) method. A 19 mm virgin aggregate and a virgin PG64-22 asphalt were used for the recycled mix and a normal (control) mix confirming WC-4 mixture gradation. The asphalt binder was recovered from the RAP by Abson method and absolute viscosity (AV) was measured from the recovered binder. Gel-permeation chromatography (GPC) test was used to measure the large molecular size (LMS) of binder from the dissolution of mix particle without binder recovery. Five AV values from AP5 binder and short-term aged (STA) mixes (original, RTFO, PAV, 3-h and 4-h STA at 180°C) and 5 LMS values were measured from the same 5 materials for regression analysis. The regression result showed a very high correlation with R2 > 0.98. Therefore, it was possible to estimate AV by LMS, which can be measured from mixture particles without binder recovery. The binder AV of recycled mix was estimated by LMS and the estimated AV (EAV) was used to evaluate rejuvenation level of recycled mix. The EAV of the recycled mix without using BWR (0%) was 9,166p, and was reduced down to 6,886p (24.9% drop) by using STM method. The average EAV in 5 BWR-ratio mixes (0, 2, 3, 4 and 5%) was 23.25% reduced by using STM method. The binder in RAP could be rejuvenated definitely better by STM and the binder EAV in recycled mixes using 3% BWR passed the limit of AV ≤ 5,000p set forced by Korean guide. Therefore, the STM must be used for all recycled mix production, i.e., the RAP, virgin binder and rejuvenator should be blended as the first stage mixing, and then the heated virgin aggregates are added for the next stage mixing. - COLLAPSE
-
Effect of stage mixing on rejuvenation level of binder in warm-mix recycled asphalt mixture
-
Scientific Paper
-
Improving the Accuracy of Pothole Tracking and Prediction using Spiking Neural Network
Spiking Neural Network를 활용한 포트홀 추적 및 예측정확도 향상 연구
-
Byeong-Hun Woo, Kyung-Suk Yoo, Jae-Soon Choi
우병훈, 유경석, 최재순
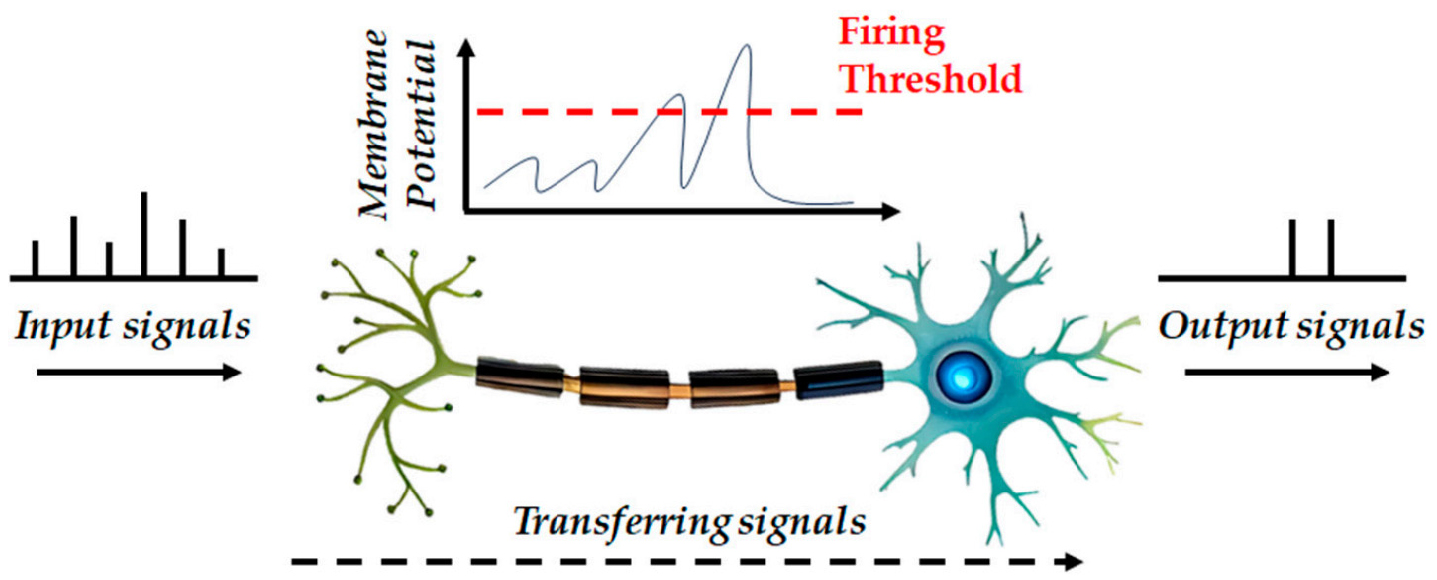
- This study explored the use of Spiking Neural Network (SNN) for tracking and predicting potholes in road pavements. SNNs are designed to …
- This study explored the use of Spiking Neural Network (SNN) for tracking and predicting potholes in road pavements. SNNs are designed to imitate the functioning of human brain neurons, offering a lightweight and fast alternative to traditional neural networks. This study utilized 500 pothole images from Kaggle, with 80% used for training and 20% for testing. The training data were analyzed using histograms, and parameters such as skewness, kurtosis, average, max frequency, and variance were set to enhance learning and prediction accuracy of SNN. The training results demonstrated that SNN could train on 400 images in approximately 1.3 seconds. The pothole detection accuracy was 0.86 for pothole image cases, while the non-pothole image cases showed the accuracy of 0.167. This was attributed to shadows and other artifacts on the asphalt surface. The results indicated that the applicability of SNN for pothole detection has a high potential. - COLLAPSE
-
Improving the Accuracy of Pothole Tracking and Prediction using Spiking Neural Network
-
Scientific Paper
-
Statistically Acceptable Process Mean of Deformation Strength for Field Asphalt Mixture
현장 아스팔트혼합물 변형강도의 통계적 공정평균 허용기준(안) 연구
-
Jong-sup Lee, Wonbae Kim, Kwang W. Kim
이종섭, 김원배, 김광우
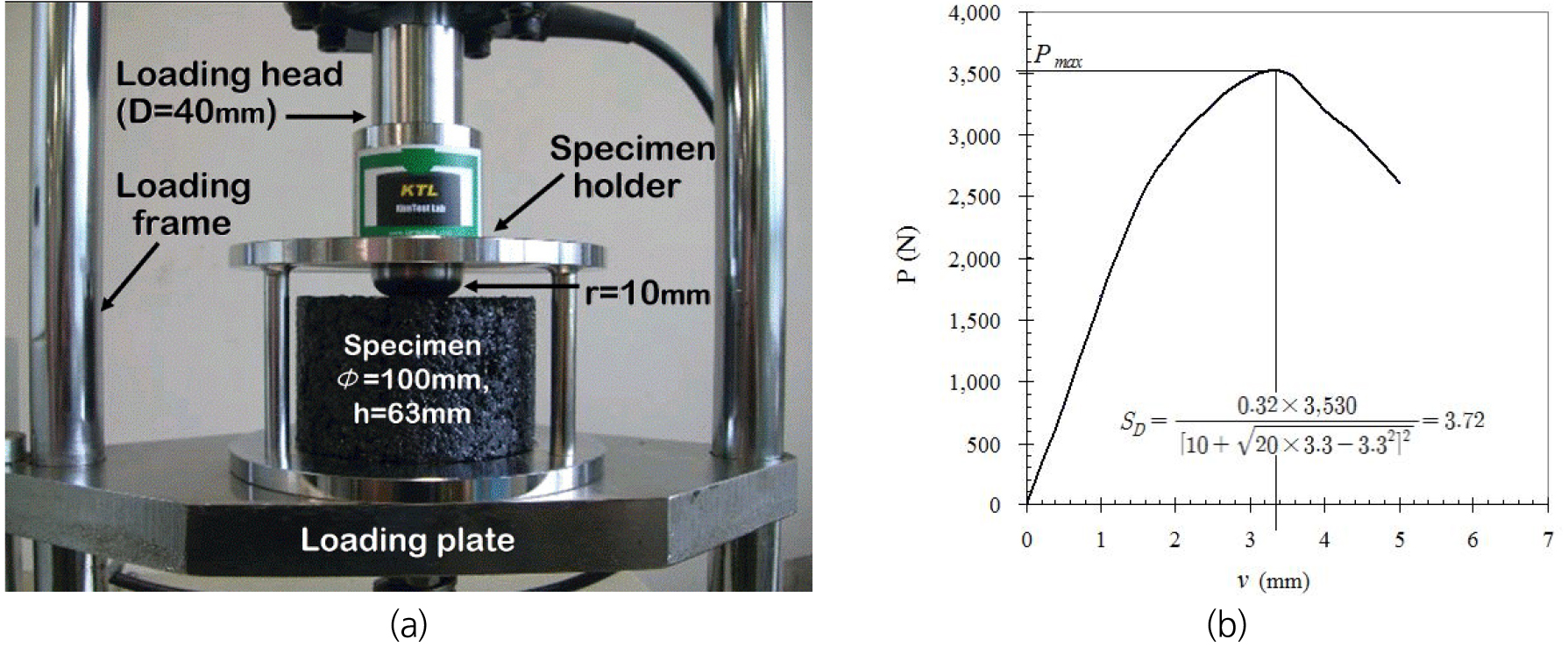
- In this study, the deformation strength (SD) was implemented as a statistical quality control criterion for field asphalt mixture …
- In this study, the deformation strength (SD) was implemented as a statistical quality control criterion for field asphalt mixture for reducing rutting of asphalt pavement because SD is a property showing high correlation with rut resistance of asphalt mixes. If the asphalt mix showing a high probability of passing SD ≥ 3.2 MPa (the mix-design criterion) is paved in the surface course of normal asphalt pavement, the pavement will have to show a strong resistance against rutting. Assuming SD population follows a Normal distribution, the 3.2 MPa was set up as the critical value (SDcr) to pass, and the coefficient of variation (VC) of field mix is considered to be 12%. The process mean (x̅) of field mix based on the standard deviation derived from VC = 12% and the probability of failure (Pf) 0.1 was determined to be 3.51 MPa. To verify the proposed x̅ field-mix samples were randomly collected from 24 locations around country, and the SD was measured from field samples. The statistical analyses showed that the Vc was found to be relatively low level, 10.20%, which is very close to the Vc = 10%. The Pf for passing 3.2 MPa was 0.09072, which is very close to Pf = 0.1. Therefore, based on these field statistics of VC = 10% and Pf = 0.1, the x̅ was modified to be 3.46 MPa. Since this value of 3.46MPa is x̅ limit, if the field mix is managed by the strength quality control (QC) using this limit, the 90% of asphalt mix will pass the 3.2 MPa, and only 10% will fail to pass the limit. If this QC is introduced, the contractor will have to pay attention for preparing strong enough materials from mix-design stage to field strength QC inspection successfully. - COLLAPSE
-
Statistically Acceptable Process Mean of Deformation Strength for Field Asphalt Mixture
-
Scientific Paper

-
2-Dimensional numerical analysis application of various countermeasure methods against liquefaction-induced settlements in highway embankments
도로 제방의 다양한 액상화 침하 대책공법의 2차원 수치해석적 적용 연구
-
SuWon Son, George Mariano A. Soriano, JinMan Kim
손수원, 조지소리아노 마리아노, 김진만
- In this paper, different liquefaction mitigation methods were analyzed in terms of the reduction in the settlement of embankment crest and the …
- In this paper, different liquefaction mitigation methods were analyzed in terms of the reduction in the settlement of embankment crest and the development of excess pore pressures. The study modeled various method for reducing settlement and pore pressure such as Dynamic Compaction, Jet Grouting, Sheet Pile Enclosure, and Gravel Drain. The soil and structure material models employed were the Mohr-Coulomb, Hardening Strain, and UBC3D-PLM for the embankment, rolled fill, and the liquefaction sand respectively. Various construction methods were modeled from 3-Dimension to 2-Dimension, and numerical analysis application methods for selecting an appropriate soil constitutive model for settlement and pore pressure analysis were summarized. Based on the numerical analysis results, settlement and pore water pressure according to each method were analyzed, and limitations of the numerical analysis application method were explained. - COLLAPSE
-
2-Dimensional numerical analysis application of various countermeasure methods against liquefaction-induced settlements in highway embankments
-
Scientific Paper
-
Evaluation of Optimal Synthetic Fiber Quantity Estimation for Synthetic Fiber-Reinforced Shotcrete for Field Applicability Assessment
합성 섬유보강 숏크리트의 현장 적용성 검토를 위한 최적 합성섬유 혼입량 평가
-
Kyung Suk Yoo, JangTae Kim, JaeSoon Choi
유경석, 김장태, 최재순
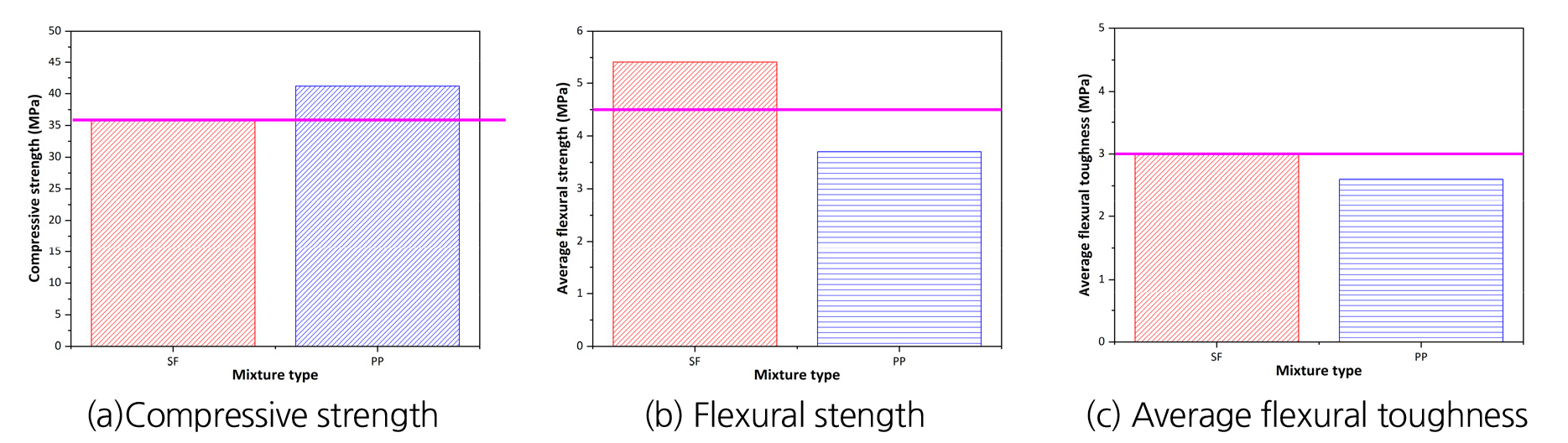
- Shotcrete technology has demonstrated its multifaceted benefits in tunnel applications, including slope protection, weathering prevention, stress dispersion, pressure relief, and arching effects. …
- Shotcrete technology has demonstrated its multifaceted benefits in tunnel applications, including slope protection, weathering prevention, stress dispersion, pressure relief, and arching effects. In response to the growing demand for enhanced flexural strength, this study investigates various fiber-reinforced shotcrete standards and compares the quality characteristics of steel, synthetic fibers, and other materials. Notably, polyethylene terephthalate (PET) fiber emerges as a promising choice due to its superior environmental performance. The research includes extensive flexural strength tests conducted at multiple sites to assess PET fiber’s suitability for practical field applications. Results indicate that PET fiber outperforms polypropylene (PP) fiber in terms of flexural toughness, constructability, and abrasion resistance. Further experiments are conducted to determine the optimal mixing rate of PET fiber, culminating in a recommended design dosage of 9 kg/m³ for effective field implementation. By evaluating the optimal quantity of PET fiber reinforcement, this study anticipates increased utilization in tunnel construction projects, thereby contributing to the advancement of fiber-reinforced shotcrete technology. - COLLAPSE
-
Evaluation of Optimal Synthetic Fiber Quantity Estimation for Synthetic Fiber-Reinforced Shotcrete for Field Applicability Assessment
-
Scientific Paper
-
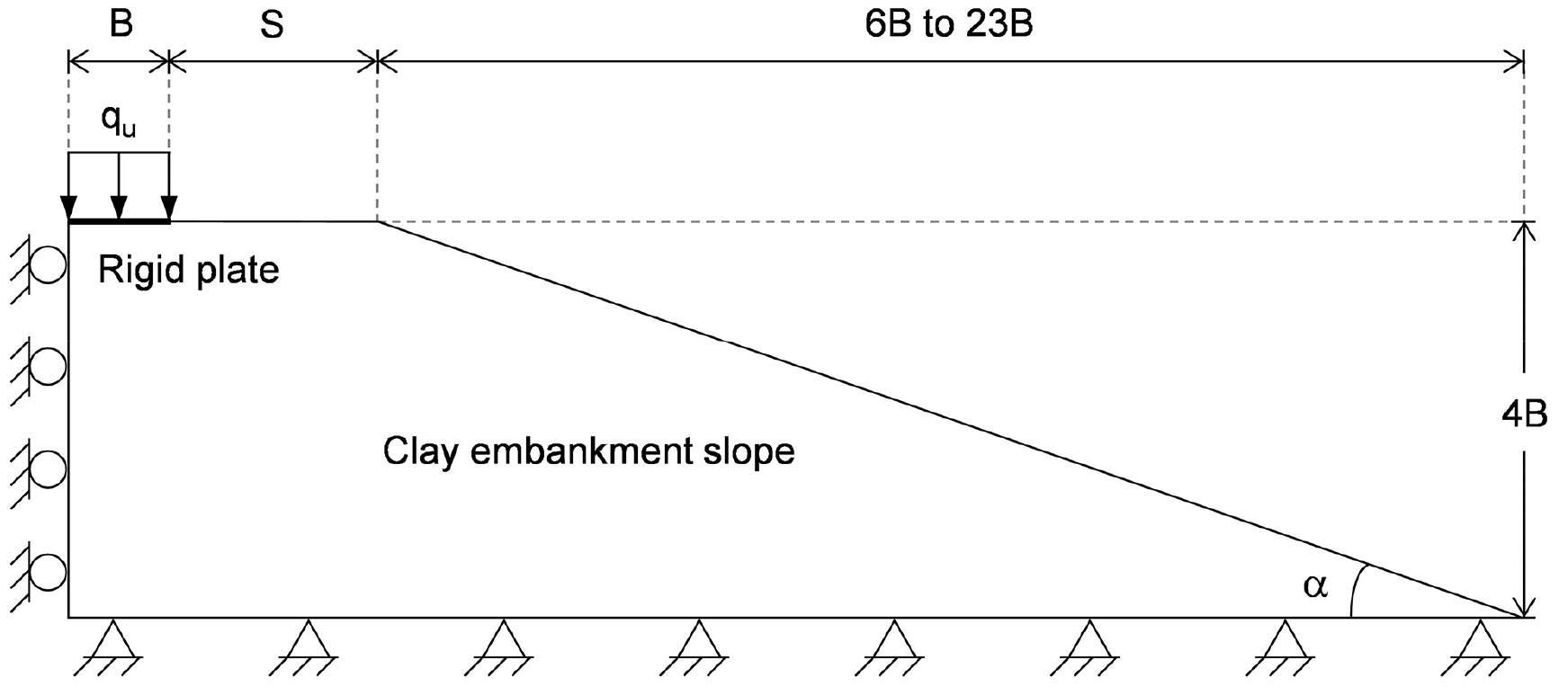
Estimation of bearing capacity of rigid pavements on nonhomogeneous embankment slopes
불균질 비탈면 제방에 놓인 강성포장의 극한지지력 평가
-
Seong Hwan Hwang, O Il Kwon, Yong Hyuk Choi, Jeong Sik Choi, Joon Kyu Lee
황성환, 권오일, 최용혁, 최정식, 이준규
- Rigid pavements are a type of road structures that provide a durable surface for vehicular traffic. This paper presents the results of …
- Rigid pavements are a type of road structures that provide a durable surface for vehicular traffic. This paper presents the results of numerical investigation into the bearing capacity for rigid pavements over embankment slopes of both homogeneous and linearly increasing shear strength profiles. Finite element limit analysis is used to obtain the undrained bearing capacity factors (Nc) and fail mechanisms of the pavement-soil system, accounting for the effect of setback distance ratio (S/B), slope angle (a), and nonhomogeneous strength ratio (kB/su0). The results indicate that the bearing capacity increases with an increase in S/B and kB/su0, while it decreases with an increase in a. The setback distance beyond which the pavement does not affect the bearing capacity is identified. - COLLAPSE
-
Estimation of bearing capacity of rigid pavements on nonhomogeneous embankment slopes
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of the Korean Asphalt Institute
Journal of the Korean Asphalt Institute
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of the Korean Asphalt Institute
Journal of the Korean Asphalt Institute









