-
Technical Notes
-
Technical feasibility of EMAS pavement in light of the Muan Airport overrun: A review of international applications
무안공항 사고를 계기로 본 EMAS 포장의 기술적 타당성과 해외 적용 사례 고찰
-
In Woo Shin, Kyong Il Ko, Dong Min Cho
신인우, 고경일, 조동민
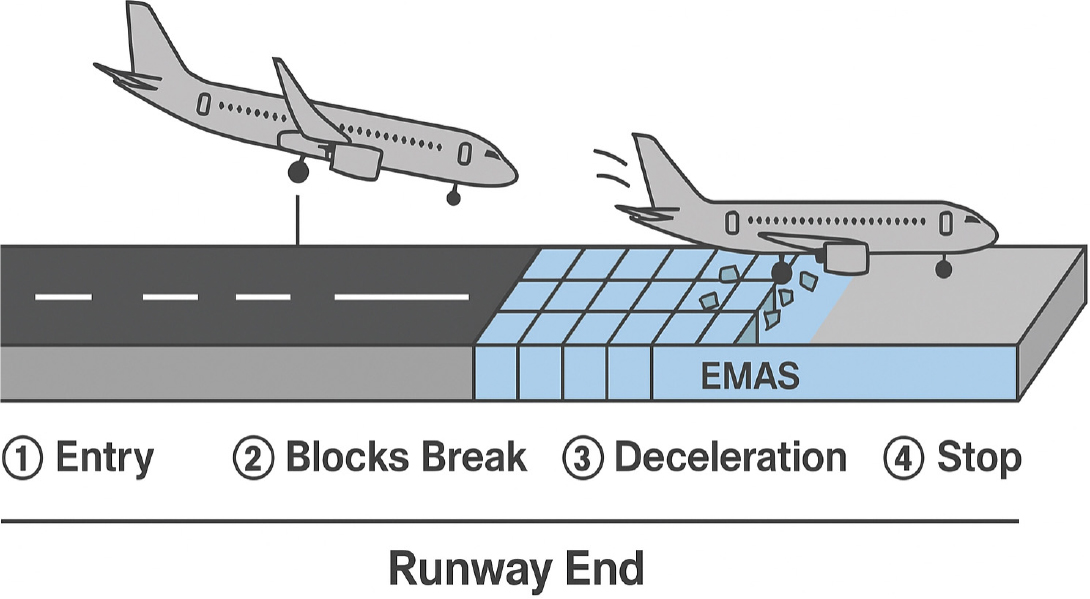
- On December 29, 2024, Jeju Air Flight 7C2216 overran the runway during an emergency landing attempt at Muan International Airport, resulting in …
- On December 29, 2024, Jeju Air Flight 7C2216 overran the runway during an emergency landing attempt at Muan International Airport, resulting in the deaths of 179 out of 181 onboard. The incident revealed a critical deficiency in the runway end safety area (RESA), which fell short of the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) recommendation of 240 meters. This tragedy has reignited interest in the adoption of the Engineered Materials Arresting System (EMAS), a passive deceleration technology deployed at runway ends to mitigate overrun risks. This technical note investigates the structural design, international implementation, and policy frameworks of EMAS, focusing on its application in the United States and China. It analyzes key differences in material composition, construction methods, environmental adaptability, and regulatory certification. The paper also evaluates operational effectiveness based on real-world deceleration events and examines how EMAS has been adapted to complex topographies, such as high-altitude and high-precipitation airports in China. By comparing the FAA’s standardized framework with China’s localized MH/T 5111-2015 specification, the study highlights the importance of site-specific customization and institutional integration. The paper concludes with policy recommendations for introducing EMAS in South Korea, including the establishment of technical design guidelines, pilot site deployment, legal integration, and funding mechanisms. - COLLAPSE
-
Technical feasibility of EMAS pavement in light of the Muan Airport overrun: A review of international applications
-
Technical Notes

-
Test construction of Indonesia’s carbon-reducing, eco-friendly warm mix asphalt mixture
인도네시아 탄소저감 친환경 중온 아스팔트 혼합물의 시험시공
-
Hongjun Kwon, JaeKyu Lim, Sanghyeok Youn, Yuseung Choi
권홍준, 임재규, 윤상혁, 최유승
- A carbon reduction eco-friendly Warm-mix asphalt mixture test construction project was carried out in Sukabumi, Indonesia. The Warm mix asphalt technology, which …
- A carbon reduction eco-friendly Warm-mix asphalt mixture test construction project was carried out in Sukabumi, Indonesia. The Warm mix asphalt technology, which is manufactured at a temperature approximately 30 degrees lower than Hot mix asphalt, has the same performance as Hot mix asphalt, and it was confirmed that it has a carbon reduction effect of approximately 47% or more compared to Hot mix asphalt. - COLLAPSE
-
Test construction of Indonesia’s carbon-reducing, eco-friendly warm mix asphalt mixture
-
Technical Notes
-
Revision direction of domestic guidelines for anti-slip pavement: Technical, policy and institutional aspects based on domestic and international case studies
미끄럼방지포장의 국내・외 사례분석을 통한 국내지침의 기술/정책/제도측면의 개정방향
-
JunSeong Choi, yoonyeong Nam, Jongun Back
최준성, 남윤영, 백종은
- This technical article focuses on improving the anti-slip pavement guidelines as a practical alternative for securing the slip resistance of domestic road …
- This technical article focuses on improving the anti-slip pavement guidelines as a practical alternative for securing the slip resistance of domestic road pavements. It analyzes the technical performance and maintenance status of domestic and international application methods, including cases from advanced countries such as the United States (US), United Kingdom (UK), and Japan. Through this analysis, the article diagnoses the technical, policy, and institutional limitations of domestic guidelines and suggests a direction for revising these guidelines to ensure suitability for the domestic road environment while maintaining the effectiveness of anti-slip pavement in the long term. - COLLAPSE
-
Revision direction of domestic guidelines for anti-slip pavement: Technical, policy and institutional aspects based on domestic and international case studies
-
Scientific Paper
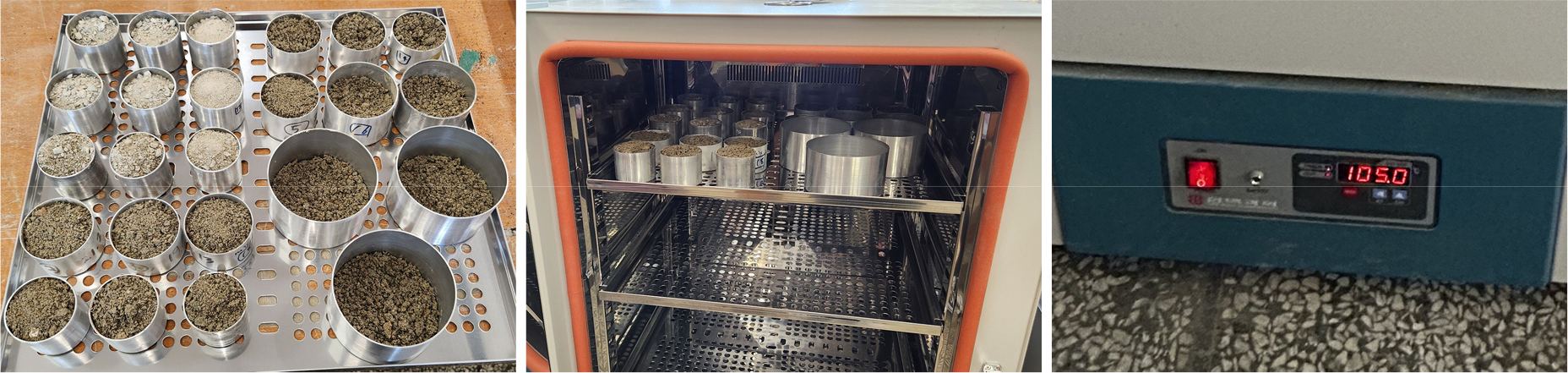

-
Evaluation of field applicability of microwave-based rapid water content measurement method in recycled aggregate production facilities
전자레인지를 이용한 급속 함수비 측정방법의 순환골재 생산시설 현장 적용성 평가
-
Min Seok Oh, Ji Hye Lee, Kyung Suk Yoo
오민석, 이지혜, 유경석
- With the increasing demand for recycled aggregates, intermediate treatment facilities that process construction waste are experiencing frequent screen clogging issues due to …
- With the increasing demand for recycled aggregates, intermediate treatment facilities that process construction waste are experiencing frequent screen clogging issues due to excessive moisture content in soil-rich raw materials. To address this, the present study evaluated the accuracy and reliability of the microwave oven drying method (ASTM D4643) for rapid water content determination, using the standard oven drying method (KS F 2306) as a reference. A total of 50 samples were tested under both laboratory (24 samples) and field (26 samples) conditions, and the deviations between the two methods were analyzed. Based on the correlation analysis of the experimental data, an empirical relationship was derived, and subsequent validation confirmed that the predicted and measured values lie within the 90% confidence interval. The rapid moisture-content test using a microwave oven requires less than six minutes, thereby shortening the testing time dramatically compared with KS F 2306, which takes 18-24 hours. Moreover, provided that electrical power is available, the microwave method can be performed immediately on site. - COLLAPSE
-
Evaluation of field applicability of microwave-based rapid water content measurement method in recycled aggregate production facilities
-
Scientific Paper
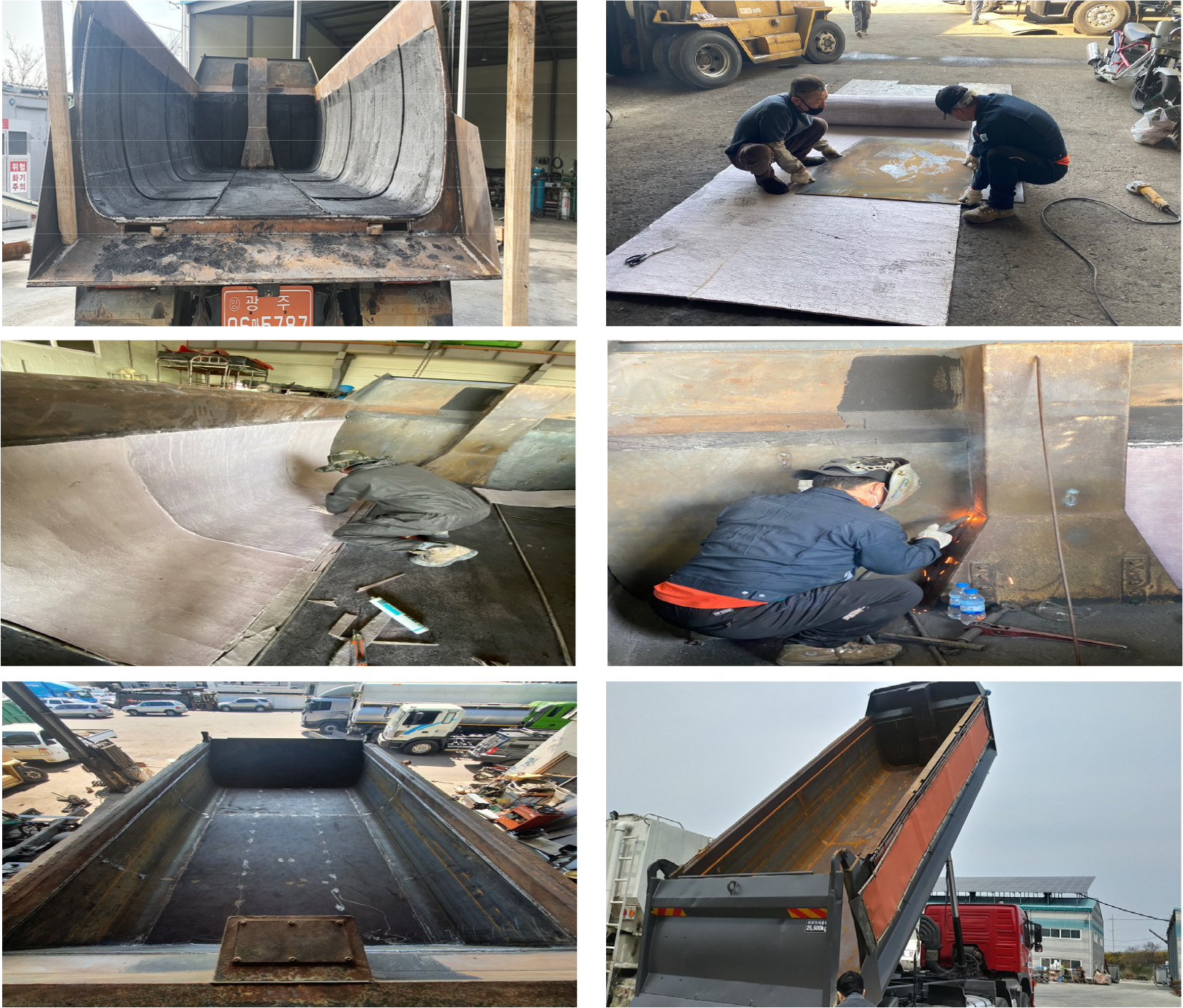

-
Performance evaluation and policy applicability of aerogel-insulated dump technology for pothole-resilient asphalt transport
아스팔트 보온 적재함을 이용한 포트홀 저감형 운반기술의 성능 분석 및 정책적 적용 가능성 연구
-
Kyong Il Ko, In Woo Shin, Dong Min Cho
고경일, 신인우, 조동민
- Asphalt pavements are increasingly susceptible to premature failures such as potholes, which not only escalate maintenance costs but also pose considerable road …
- Asphalt pavements are increasingly susceptible to premature failures such as potholes, which not only escalate maintenance costs but also pose considerable road safety risks with disaster-related implications. Potholes have been identified as major contributors to vehicular damage, motorcycle accidents, and pedestrian injuries, emphasizing the urgency for preventive technologies that enhance pavement durability. A primary cause of these failures is insufficient thermal retention of asphalt mixtures during transportation, leading to inadequate compaction and weak interlayer bonding. This study proposes and evaluates a thermally insulated dump body that incorporates high-performance aerogel between double-layered steel plates to minimize heat loss during transit. Field trials demonstrated that the insulated dump body effectively maintained asphalt mixture temperatures up to 160°C at placement, mitigating temperature drops exceeding 65°C compared to conventional dump bodies. Laboratory tests confirmed notable improvements in mixture properties: a 1.7% increase in compaction density, a 35% enhancement in indirect tensile strength, and a 37% gain in toughness. These enhancements directly translate into improved resistance to thermal cracking and fatigue-induced degradation, significantly reducing the risk of pothole formation. By extending pavement lifespan and lowering maintenance costs, this technology contributes to improved roadway safety and aligns with national disaster prevention objectives. Accordingly, this study recommends nationwide adoption via policy-driven initiatives, including its designation as certified public maintenance equipment, linkage with pilot procurement programs, and phased implementation of mandatory use standards. - COLLAPSE
-
Performance evaluation and policy applicability of aerogel-insulated dump technology for pothole-resilient asphalt transport
-
Scientific Paper
-
Current status analysis and study on measures to improving road access zone regulations
도로 접도구역 규제 개선을 위한 현황 분석 및 방안 연구
-
Hongjun Kwon, Kyejoo Na, Jongeun Baek, JaeKyu Lim
권홍준, 나계주, 백종은, 임재규
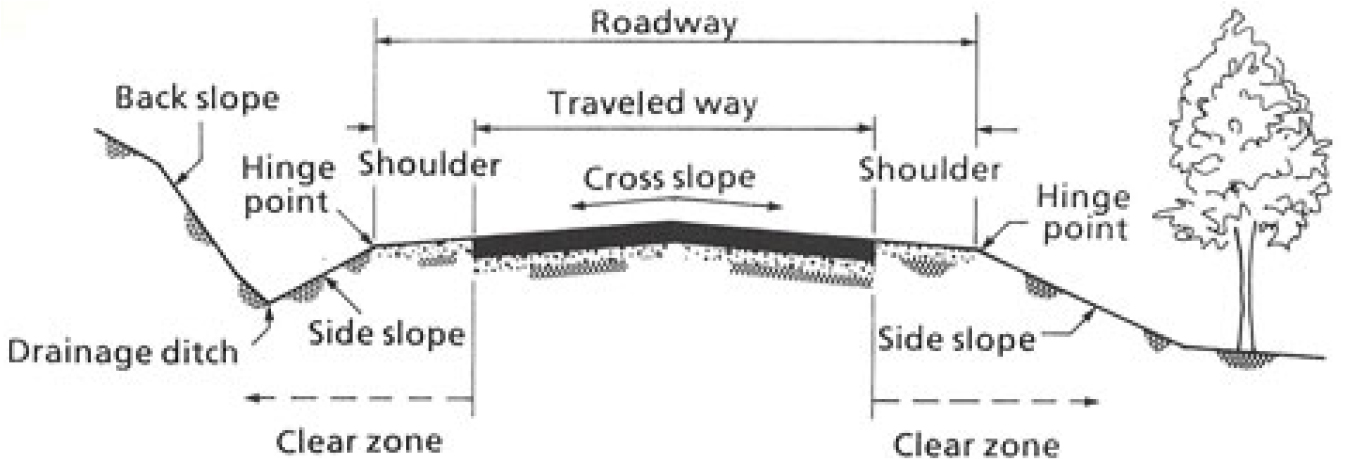
- In Korea, according to Article 40 of the Road Act (Designation and Management of Road Access Zones), road access zones are designated …
- In Korea, according to Article 40 of the Road Act (Designation and Management of Road Access Zones), road access zones are designated and managed within a certain range 10 meters on both sides for expressways and 5 meters for national and local roads from the boundary of the road zone as determined and announced under Article 25 of the Road Act. However, the excessive or uniform designation of road access zones has led to reduced land utility and increased public inconvenience due to the low threshold for purchase claims. Therefore, there is a need to improve the road access zone management system and establish more efficient management measures. This study aims to propose practical and reasonable methods for the designation of road access zones and compensation for losses, as well as to establish an information management system for the efficient management of road access zones. Specifically, the study suggests lifting the designation of road access zones that have been inappropriately assigned in cities, counties, and districts; expanding the exception criteria so that planned management areas designated for residential environment improvement may not be designated as road access zones; raising the threshold for purchase claims from 50% to 70%; providing a 50% reduction in property tax to protect citizens’ property rights; and presenting a plan for establishing an information management system to enable efficient management of road access zones between central and local governments. - COLLAPSE
-
Current status analysis and study on measures to improving road access zone regulations
-
Scientific Paper
-
Assessment of tunnel blast-induced vibration of road subgrades
터널발파에 따른 도로하부 지반진동 평가
-
Chang Hee Lim, Mun Ki Choi, O Il Kwon, Yong Hyuk Choi, Joon Kyu Lee
임창희, 최문기, 권오일, 최용혁, 이준규
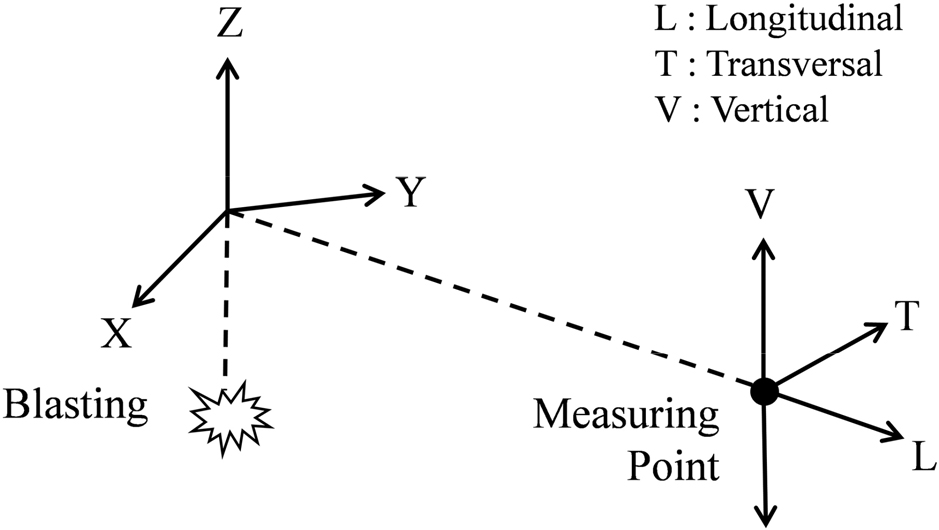
- Ground vibration induced by tunnel blasting can pose a potential hazard to infrastructures (roads, buildings and bridges) in near fields. This paper …
- Ground vibration induced by tunnel blasting can pose a potential hazard to infrastructures (roads, buildings and bridges) in near fields. This paper presents the characteristics of subgrade vibrations due to tunnel blast during railway construction. Influences of uncharged hole number and detonator type on tunnel blasting vibration are examined. Using blasting data, the site-specific relations of peak particle velocity with scaled distance are formulated at the 50% and 95% confidence levels and the performance of conventional prediction models for subgrade vibrations is evaluated. The maximun amount of explosive for allowable vibration to ensure the safety of adjacent structures is determined by applying the Korean Design Standard for tunnel excavation. - COLLAPSE
-
Assessment of tunnel blast-induced vibration of road subgrades
-
Scientific Paper
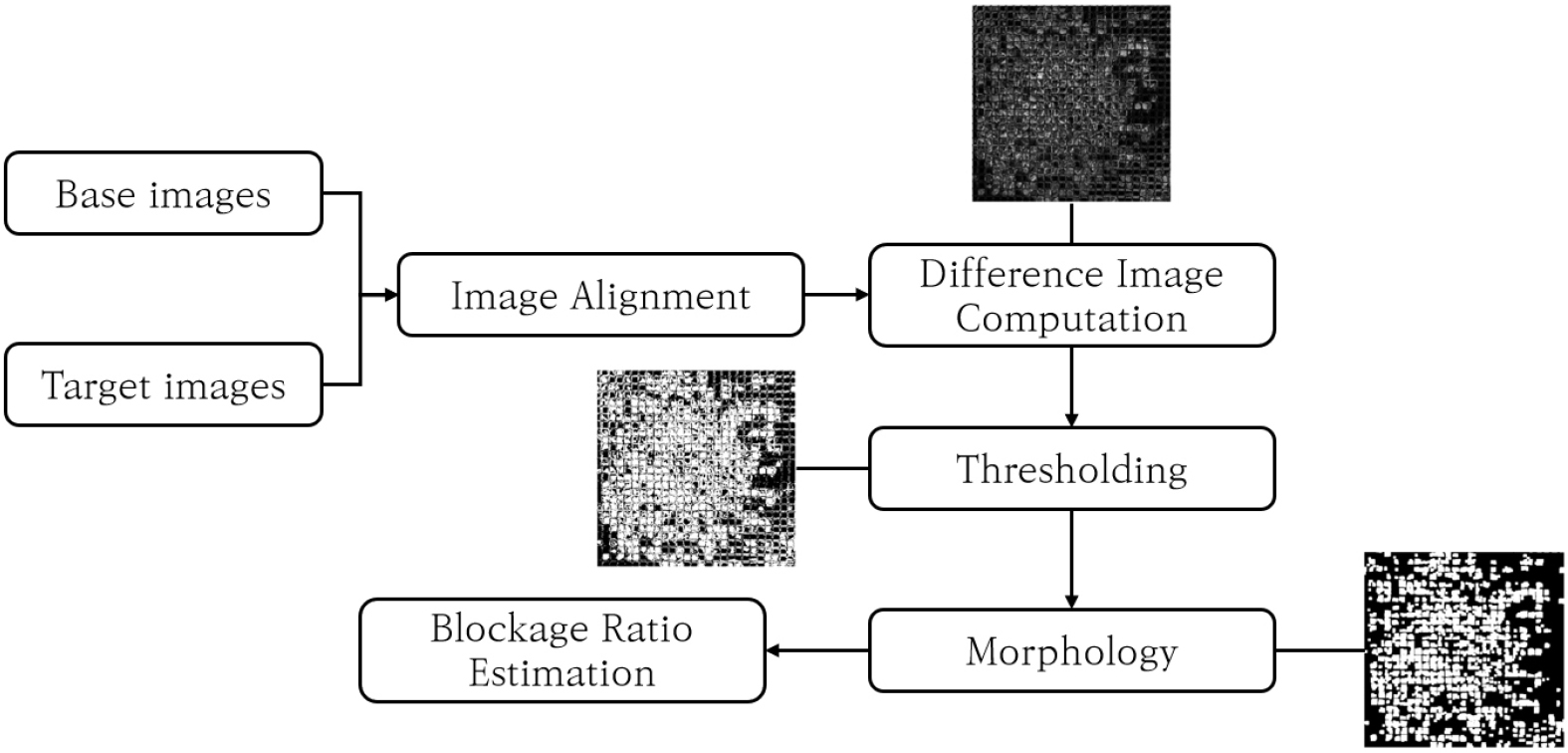
-
A study on the evaluation of screen mesh clogging ratio using difference imaging technique
차영상 기법을 활용한 스크린망 망막힘률 평가 연구
-
Min Seok Oh, Ji Hye Lee, Kyung Suk Yoo
오민석, 이지혜, 유경석
- Mesh clogging during recycled-aggregate production hampers screening efficiency and increases product variability. This study proposes an automated, quantitative assessment of clogging based …
- Mesh clogging during recycled-aggregate production hampers screening efficiency and increases product variability. This study proposes an automated, quantitative assessment of clogging based on a difference-imaging pipeline. A target image is first aligned to a reference background via an Enhanced Correlation Coefficient (ECC) rigid transformation; the resulting difference image is then conservatively thresholded and post-processed with two openings and one dilation using a 3 × 3 structuring element to obtain a binary clog mask. The clogging ratio is defined as the percentage of masked pixels within the effective aperture area derived from the reference image. For three representative cases, comparison with manually generated masks showed that absolute deviations remained within 5%, demonstrating the high consistency of the proposed method. Visual inspection further verified that the automatically generated masks accurately captured major debris distributions. A limitation arose when low-contrast debris failed to exceed the fixed threshold, indicating the need for adaptive thresholding and illumination control. By training on a large‐scale screen-mesh dataset collected under diverse environments and conditions, and by developing a deep-learning-based object-detection model capable of real-time foreign-matter detection and clogging-ratio analysis, the system can be integrated with on-site monitoring equipment to leverage real-time outputs, thereby enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of automated analysis. - COLLAPSE
-
A study on the evaluation of screen mesh clogging ratio using difference imaging technique
-
Scientific Paper
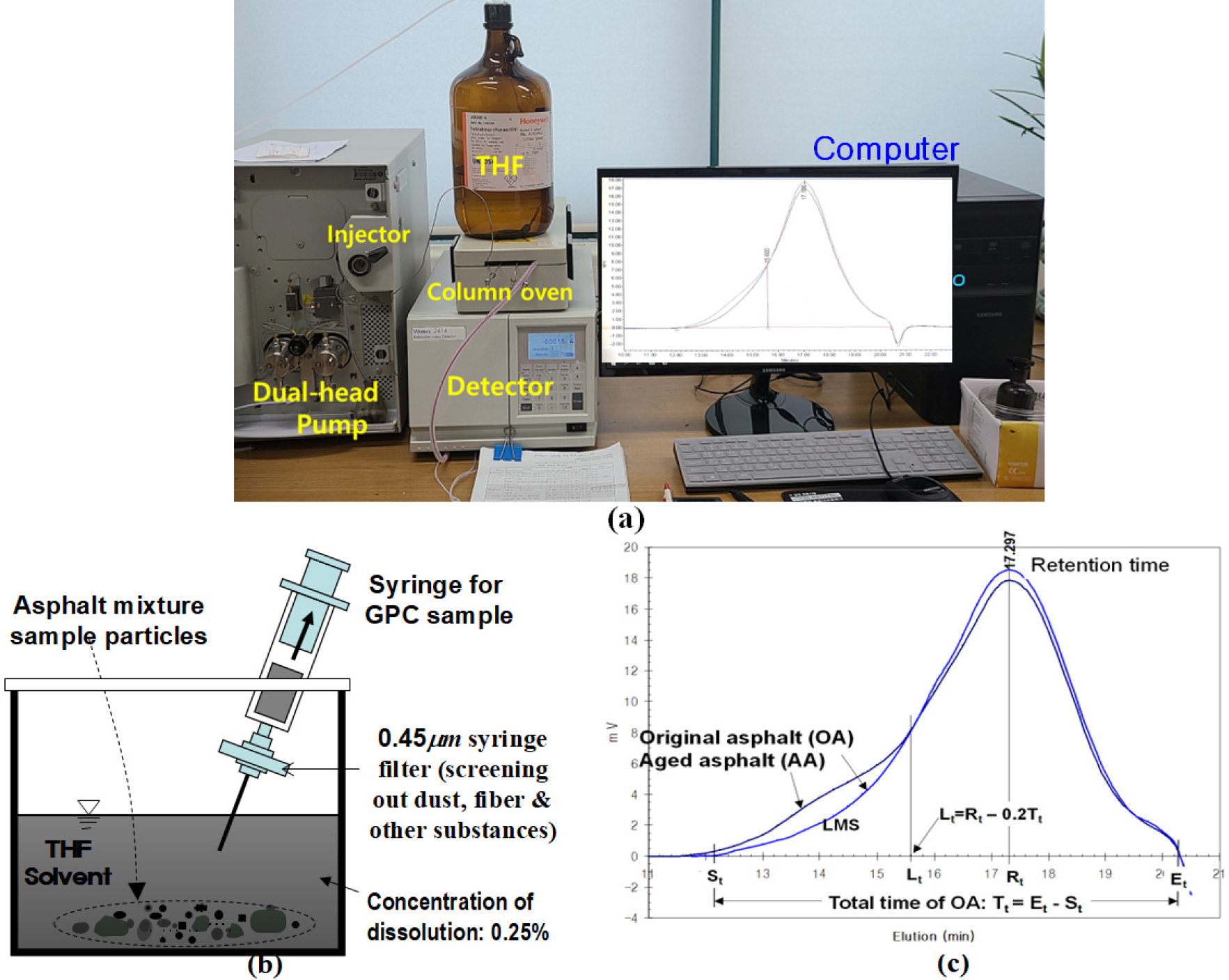
-
Comparative study for estimation methods of binder absolute viscosity in short-term aged dense-grade asphalt mixtures
단기노화 밀입도 아스팔트혼합물 바인더의 절대점도 추정 방식의 비교연구
-
Wonbae Kim, Woohyun Kim, Sungjin Lee, Mingeon Choi, Kwang W. Kim
김원배, 김우현, 이성진, 최민건, 김광우
- The hot-mix asphalt (HMA) is short-term aged during haul-and-queue before paving. The short-term aging (STA) level is mainly evaluated by absolute viscosity …
- The hot-mix asphalt (HMA) is short-term aged during haul-and-queue before paving. The short-term aging (STA) level is mainly evaluated by absolute viscosity (AV) of the recovered binder from the mix. Since measuring AV from the aged mix is time-consuming task, instead of measuring AV, several techniques were developed to get an estimated AV (EAV). In this study, two AV estimation methods were evaluated; one is gel-permeation chromatography (GPC) test and another is aging quantity (AQ) method. The GPC is chemical test measuring the ratio (%) of large molecular size (LMS) of asphalt in mixture sample. The AQ is a numerical value representing agedness quantitatively by using time (min) and temperature (°C) of STA. The target material was dense-graded normal asphalt mixture prepared using PG64-22 binder. The best-fit numerical model from the regression between AV and LMS is used to determine EAV for GPC method. The best-fit regression model between AV and AQ is used to assess EAV for AQ method. The regression analysis between two EAV data sets determined by each of the two methods showed an excellent correlation ( R 2 >0.98). Statistical t-test between two data set arrays showed no-significant difference between two EAV data sets. No-significant differences were also found from the t-tests between measured AV vs. EAV by LMS, and measured AV vs. EAV by AQ. Therefore, the EAV determined by LMS method or by AQ method was found to be a convenient estimated value in place of measured AV. - COLLAPSE
-
Comparative study for estimation methods of binder absolute viscosity in short-term aged dense-grade asphalt mixtures
-
Scientific Paper
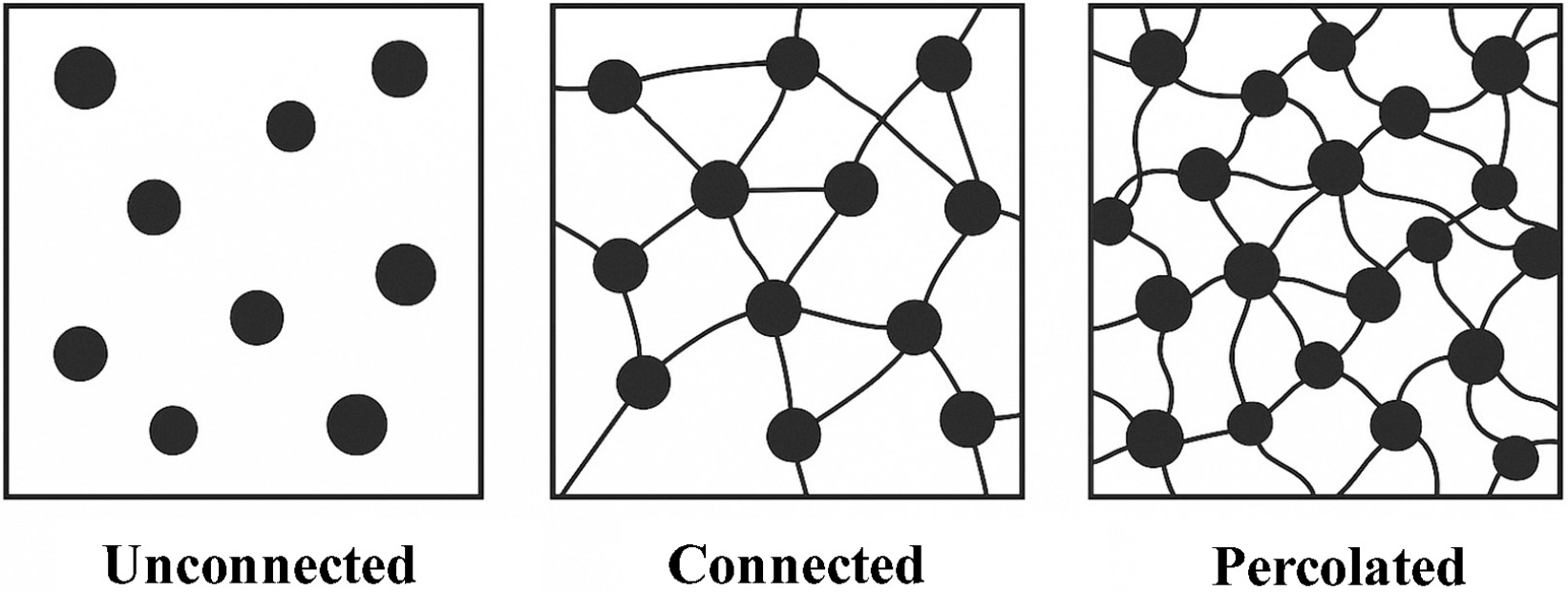
-
Investigation into the Electrical Properties of Conductive Asphalt Concrete in Korea
국내 전도성 아스팔트 콘크리트의 전기저항 특성 분석
-
Seungyeol Oh, Gun-cheol Lee, Seongwon Hong
오승열, 이건철, 홍성원
- In recent years, the growing need for intelligent infrastructure has drawn attention to multifunctional asphalt concrete technologies, particularly those capable of self-sensing, …
- In recent years, the growing need for intelligent infrastructure has drawn attention to multifunctional asphalt concrete technologies, particularly those capable of self-sensing, self-heating, and self-healing. Among these, conductive asphalt concrete, created by incorporating conductive fillers such as graphite, carbon fibers (CF), or carbon nanotubes (CNT), has emerged as a promising solution to improve road maintenance, especially under extreme weather conditions. This study reviews the current research trends and experimental findings in Korea concerning the electrical resistance characteristics of conductive asphalt mixtures. Emphasis is placed on material types, mixing ratios, experimental setups, and performance evaluation methods. Key findings from domestic studies indicate that the addition of conductive materials significantly reduces electrical resistance, and the sensitivity of resistance change to mechanical stress can enable real-time structural monitoring. For instance, CNT-CF hybrid composites have demonstrated superior conductivity and network stability compared to single-material systems. Graphite-enhanced asphalt has shown effective self-heating performance for snow melting applications, while the integration of CF into cementitious matrices has offered insights into the percolation threshold and conductive behavior under varying loading conditions. This review not only summarizes the results of electrical resistance measurement tests in Korean research but also highlights the practical limitations and future research needs. The analysis aims to provide a foundation for scaling up these technologies for field application and supports the development of smart pavement systems that align with the evolving demands of infrastructure management. - COLLAPSE
-
Investigation into the Electrical Properties of Conductive Asphalt Concrete in Korea
-
Scientific Paper
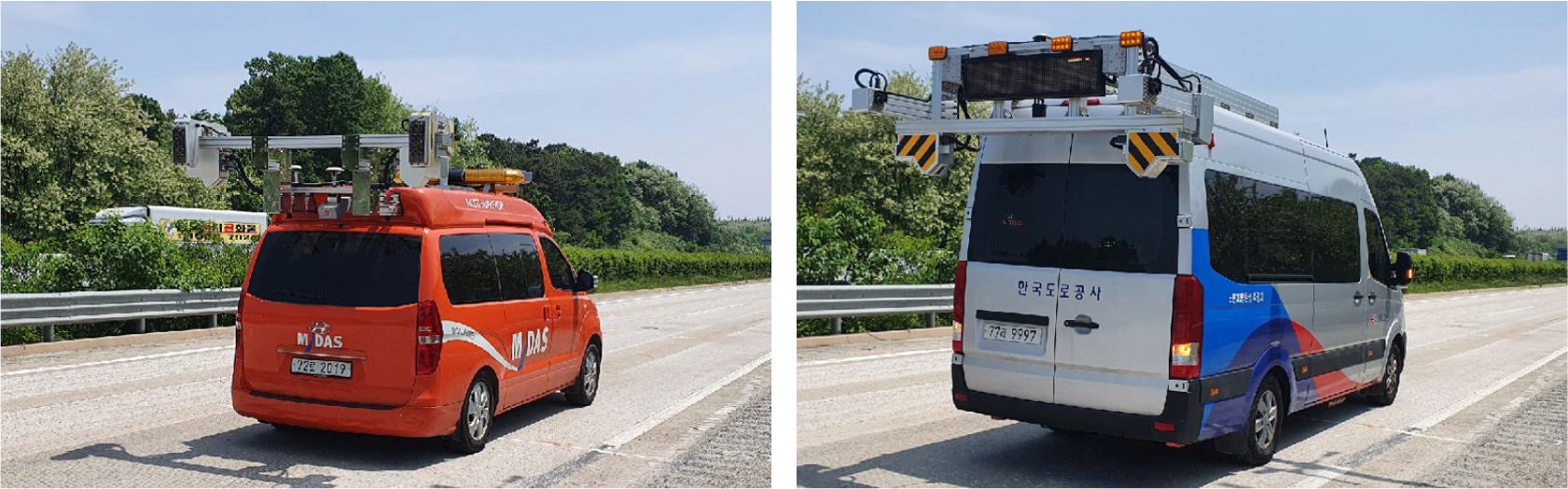

- Development of AI technology on expressway surface monitoring for advanced HPMS ecosystem
- Ki Hoon Moon, Dueck Su Sohn
- It is well known that optimized pavement thickness design skills and reliable construction technologies have been considered being significant factors for expressway …
- It is well known that optimized pavement thickness design skills and reliable construction technologies have been considered being significant factors for expressway in South Korea till early 2,000. However, a proper management and rehabilitation efforts of existing expressway rather than building new lanes became an important factor after 2,005 after total length of constructed expressway exceeded more than 3,000 km, approximately. One of good examples for the mentioned efforts is rising of HPMS (i.e. Highway Pavement Management System) concept, trials and corresponding applications. In HPMS, the most important factor is: surveying and analyzing existing expressway surface condition with reasonable, reliable and efficient manner. Due to this reason, application of various advanced technologies on HPMS area were considered since early 2010. For the past decades, many advanced technologies such as AI(i.e. Artificial Intelligence) modeling approach and corresponding physical equipment were considered to be applied on roadway condition monitoring and analysis procedure. By applying AI technologies in HPMS business area, two major things can be achieved: first, an automated pavement surface monitoring work for efficiency and secondly, saving current huge HPMS management budget through more efficient and reliable surveying results. In this paper, the feasibility of applying AI based pavement surface monitoring and analysis technology was considered. As a result, AI based pavement surface monitoring and analysis tool provided a reasonable and reliable results compared to the conventional analysis approach. This finding provides a promising signal that more AI based technologies can successfully applied in HPMS business area in the next future. - COLLAPSE
-
Scientific Paper

-
Effect of laboratory compaction methods and curing conditions on the strength of cold in-place recycling mixture with bubble asphalt
실내 다짐방법 및 양생조건이 상온 현장 재활용 기포 아스팔트 혼합물의 강도에 미치는 영향
-
Yongjoo Kim
김용주
- Asphalt pavements are prone to deterioration and aging due to environmental factors such as sunlight, rainfall, and snowfall, as well as repeated …
- Asphalt pavements are prone to deterioration and aging due to environmental factors such as sunlight, rainfall, and snowfall, as well as repeated traffic loading. Consequently, regular maintenance and rehabilitation are essential. In many countries, cold in-place recycling (CIR) with bubble asphalt has been actively adopted as a sustainable asphalt pavement rehabilitation method. This technique involves milling aged asphalt pavement on-site, mixing it with bubble asphalt at ambient temperature, and immediately repaving. However, in Korea, a standardized mix design procedure specifically for CIR mixtures with bubble asphalt has not yet been established, and the procedure for plant cold recycled asphalt mixtures is currently being applied by extension. This study investigates the effects of laboratory compaction methods (Marshall compaction and Gyratory compaction) and curing temperatures (40°C to 60°C) on the volumetric properties and indirect tensile strength (ITS) of CIR mixtures with bubble asphalt. Depending on the reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) sources and the bubble asphalt content, the number of Gyratory compaction equivalent to 75 blows of Marshall compaction ranged from 15 to 43. Moreover, specimens cured at 60°C for 2 days exhibited 20% to 30% higher indirect tensile strength (ITS) compared to those cured at 40°C for 3 days. The findings highlight that laboratory compaction methods and curing conditions significantly affect the mechanical strength of CIR mixtures with bubble asphalt and must be considered in developing an appropriate mix design procedure for CIR mixtures. - COLLAPSE
-
Effect of laboratory compaction methods and curing conditions on the strength of cold in-place recycling mixture with bubble asphalt
-
Scientific Paper
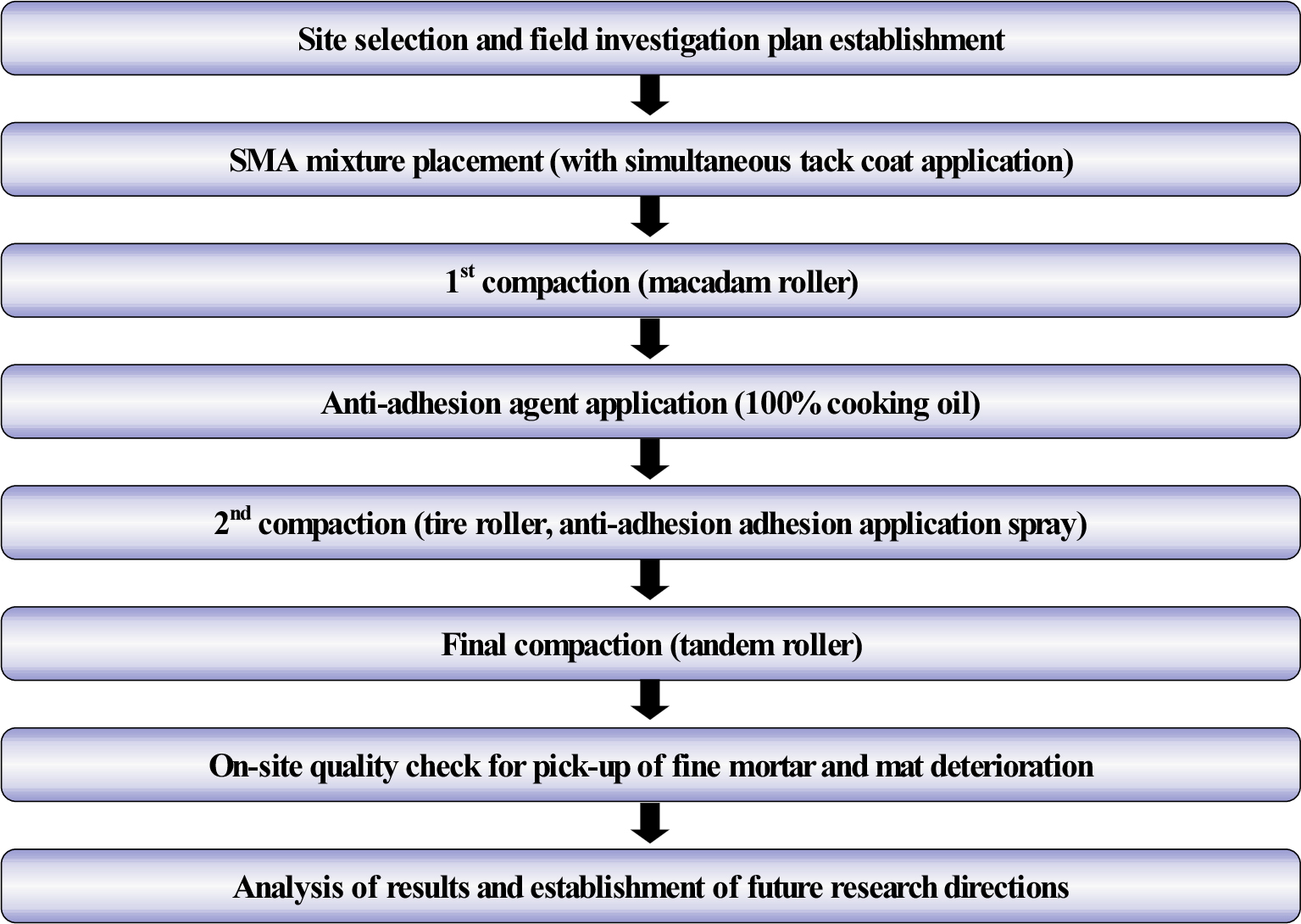
-
A basic study on the mix design and field compaction process of SMA pavements for appropriate performance
SMA 포장의 적정성능 구현을 위한 실내 배합설계 및 현장 다짐 공정 개선에 관한 기초 연구
-
JunSeong Choi, Jongeun Baek, YeJi Jung, Jongseong Park
최준성, 백종은, 정예지, 박종성
- This study aims to establish a systematic VCA(Voids in Coarse Aggregates)-based mix design and compaction procedure to optimize the performance of Stone …
- This study aims to establish a systematic VCA(Voids in Coarse Aggregates)-based mix design and compaction procedure to optimize the performance of Stone Mastic Asphalt (SMA) pavements. The mix design process focuses on quantitatively evaluating coarse aggregate interlocking to enhance structural stability and resistance to rutting. Laboratory tests were conducted to determine dry-rodded VCA ( V C A D R C ) and mixture VCA ( V C A M I X ) values based on ASTM C29 procedures, with the optimal mix satisfying the interlocking condition of V C A M I X < V C A D R C . Volumetric properties were also evaluated to select the optimal asphalt content. In addition, field trials incorporating tire rollers were performed to assess the applicability of the proposed design in actual construction conditions. The results demonstrate that the VCA-based mix design framework effectively improves aggregate interlocking and structural performance, while tire roller application further contributes to achieving consistent compaction quality on site. This integrated approach provides a practical foundation for enhancing the durability and reliability of SMA pavements. - COLLAPSE
-
A basic study on the mix design and field compaction process of SMA pavements for appropriate performance
-
Scientific Paper
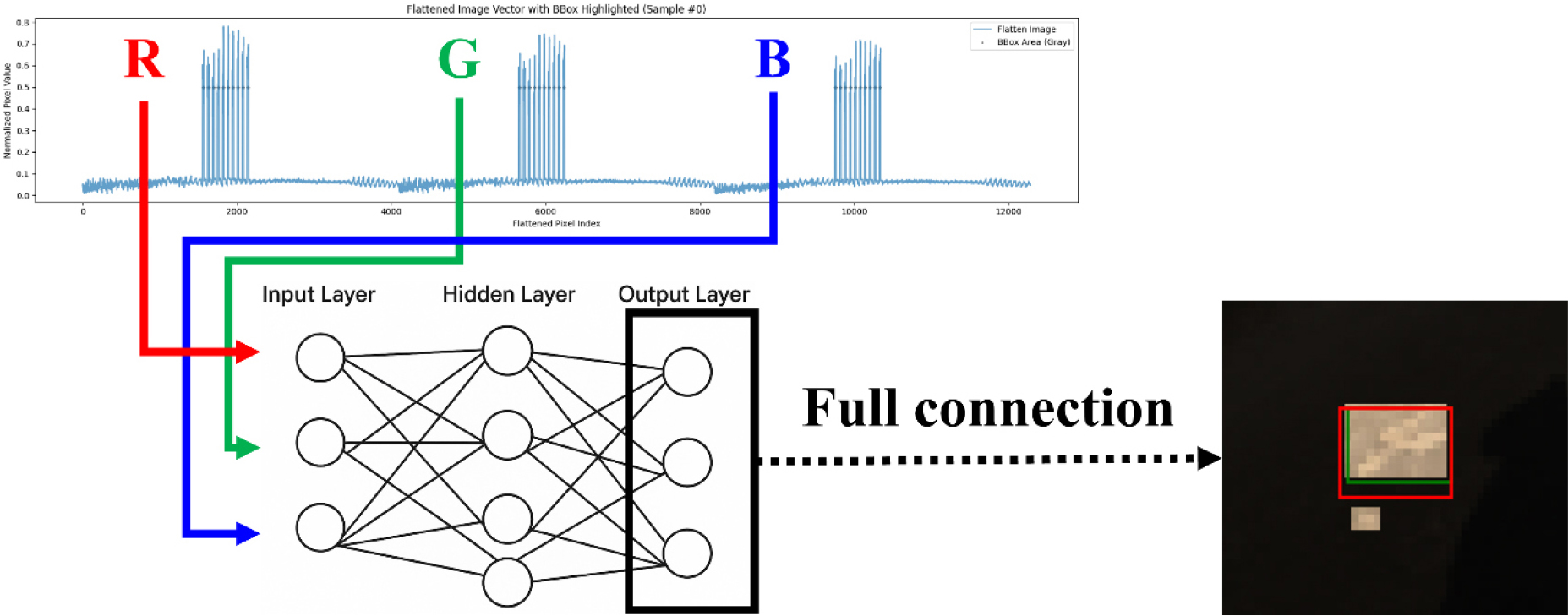
-
Selective area emphasis preprocessing of images for pothole detection in asphalt pavement
이미지의 선택적 영역 강조 전처리를 활용한 아스팔트 도로포장 포트홀 탐지 연구
-
Joo-Young Kim, Jae-Suk Ryou, Byeong-Hun Woo
김주영, 유재석, 우병훈
- This study presents a lightweight machine learning approach for pothole detection in asphalt pavements using selective region highlighting preprocessing and an artificial …
- This study presents a lightweight machine learning approach for pothole detection in asphalt pavements using selective region highlighting preprocessing and an artificial neural network (ANN) architecture. Unlike the existing CNN-based methods that require high computational resources and GPU acceleration, this study presents an efficient alternative that maintains competitive detection accuracy. The method reduces pixel intensities in areas without potholes to 1/10 of the original while preserving labeled bounding box regions. By flattening RGB image data and processing it through a simple ANN structure, the model effectively learns key features for object detection. 467 labeled images and 133 validation images from Roboflow were used for training, with a size of 64 × 64 × 3. The results show a stable learning process with a low loss rate and a high R2 value. The model achieved an average IoU of 0.5373 during testing and showed IoU values above 0.6 in well-detected cases. However, the performance deteriorates in poorly detected cases, suggesting the need for further structural improvements to filter out false positives. Overall, this study demonstrates that CNN-free models can be utilized for image-based defect detection, providing promising directions for future lightweight and accessible pavement monitoring systems. - COLLAPSE
-
Selective area emphasis preprocessing of images for pothole detection in asphalt pavement
-
Scientific Paper

-
Evaluation of the physical properties of lean concrete mixtures for unpaved road improvement
비포장도로 개선을 위한 린 콘크리트 혼합물의 물리적 특성 평가
-
Ilhwan Kang, YongJoo Kim, Kanghun Lee
강일환, 김용주, 이강훈
- In Lao PDR, the majority of the road network comprises unpaved roads constructed on lateritic soils. During the dry season, these roads …
- In Lao PDR, the majority of the road network comprises unpaved roads constructed on lateritic soils. During the dry season, these roads generate excessive dust, while in the rainy season, their bearing capacity diminishes, resulting in erosion, rutting, and poor surface evenness—ultimately compromising road functionality. Considering the relatively easy availability of cement in the region and the function of unpaved roads as connectors between rural villages and major arterial roads, lean concrete (LC) emerges as a promising alternative for unpaved road improvement. However, no prior research or field applications of LC in this context have been reported, underscoring the need for a systematic investigation of its fundamental material properties. This study employed locally sourced construction materials in Laos to produce lean concrete in accordance with the Korean standard KCS 44 50 15. Cylindrical specimens (ø150 × 300 mm) were prepared, and tests were conducted to evaluate compressive strength, elastic modulus, splitting tensile fatigue performance, and the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) at curing ages of 3, 7, 14, 28, and 90 days. The results confirmed that the LC mix met the KCS-specified target compressive strength of 5.0 MPa and showed continuous strength development up to 90 days. Owing to its low cement content, the LC exhibited comparatively lower elastic modulus, tensile strength, and thermal expansion than conventional concrete. The findings from this study provide foundational data for structural analysis of LC pavement under Lao environmental conditions and serve as a basis for evaluating traffic-induced fatigue and long-term performance. - COLLAPSE
-
Evaluation of the physical properties of lean concrete mixtures for unpaved road improvement
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of the Korean Asphalt Institute
Journal of the Korean Asphalt Institute
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of the Korean Asphalt Institute
Journal of the Korean Asphalt Institute









